Top Ten Serious Causes of Abdominal Pain
0 Comments
Aortic Dissection
The sudden onset of sharp pain felt in the chest is a distinctive sign of an aortic dissection. The aorta is the largest blood vessel in the body. It arises from the left ventricle of the heart, moves up through the chest, and branches off in two directions. The ascending aorta goes toward the head while the descending aorta goes toward the abdomen. A tear or dissection in the inner lining layer of the aorta is a potentially life threatening condition. The associated pain can be described as stabbing, tearing or ribbing. It can be felt below the chest bone and progresses toward the shoulders, neck, jaw, back, arms, abdomen and hips. Typically, pain that radiates to the arms and legs indicates worsening of the dissection. Photo: Getty Images
Acute Intestinal Ischemia
The sudden onset of pain, ranging from mild to severe, accompanied with the urgent need to have a bowel movement, is the hallmark of acute intestinal ischemia. Decreased blood supply to the intestines is the cause of intestinal ischemia. Both the small and large intestines can be effected. Adhesions, hernias, atherosclerosis, blood clots and low blood pressure increase the risk of intestinal ischemia. It is a serious medical condition that can lead to death if not properly treated. Photo: Getty Images
Acute Mesenteric Ischemia
The sudden onset of severe abdominal pain associated with no other symptoms is the early sign of mesenteric ischemia. It is a rare disorder that is challenging to diagnose. Acute mesenteric ischemia is the interruption of intestinal blood flow. The intestinal mucosa requires a high blood flow to meet its high metabolic rate. Ischemia or decreased blood flow disrupts the protective mucosal barrier causing a release of bacteria, toxins and substances that control dilation and constriction. Necrosis, or tissue death, can occur as early as 10 to 12 hours after the onset of symptoms. Photo: Getty Images

Intussusception
The sudden onset of intense abdominal pain is the first sign of intussusception, an abdominal emergency generally affecting children under 2 years old. The severe abdominal pain is usually intermittent but can reoccur, increasing in both intensity and duration. The warning sign is a loud, anguished crying. A child may draw the knees to the chest while crying. Intussusception results when one part of the intestine slides into the next portion. Consequently, it creates a blockage which leads to decreased blood flow, irritation and swelling. Decreased blood flow leads to intestinal tissue death. As the condition progresses, a child becomes weaker, develops a fever and can go into shock. Photo: Getty Images
Intestinal Obstruction
Intermittent abdominal cramping associated with abdominal swelling, nausea and vomiting can be indicative of an intestinal obstruction. A blockage of the colon can be caused by a variety of conditions including adhesions or scar tissue that forms after surgery, ingested materials or tumors. A partial or complete intestinal obstruction prevents intestinal contents to pass through. Untreated, it can lead to electrolyte imbalances, infection and perforation of the intestine. Photo: Getty Images
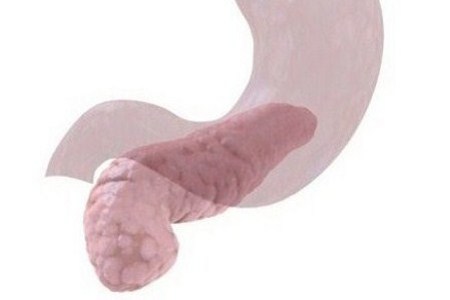
Acute Pancreatitis
Gradual or sudden pain felt in the upper abdomen, that may extend to the back, is an early warning sign of acute pancreatitis. It is inflammation of the pancreas, which is a large gland located behind the stomach and adjacent to the duodenum. Gallstones that pass through the common bile duct are the most common cause of acute pancreatitis. The pain may be mild at first and feel worse after eating. Most often, the pain is severe, constant and lasts for several days. With proper treatment, inflammation resolves in a few days. However, acute pancreatitis can be a life-threatening illness with serious complications such as infection and kidney failure. Photo: Getty Images
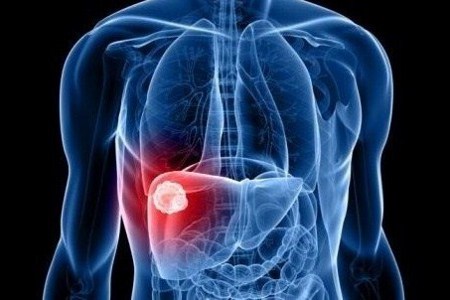
Tumors
Tumors, either malignant or benign, occur when cells go awry, dividing excessively. Abdominal pain is a symptom of tumors that form on organs and glands located in the abdominal cavity. Fibroid tumors cause extreme pain when they grow beneath the lining of the uterus and when they degenerate. Adrenal cancer, which is a rare form of cancer that develops in the adrenal glands, located on top of the kidneys, can manifest with persistent abdominal pain. Upper abdominal pain that radiates to the back is a symptom of advanced pancreatic cancer. Upper abdominal pain associated with nausea and vomiting is just one symptom of stomach and liver cancers. Upper right quadrant abdominal pain associated with weight loss and jaundice is a symptom of gallbladder cancer. Photo: Getty Images
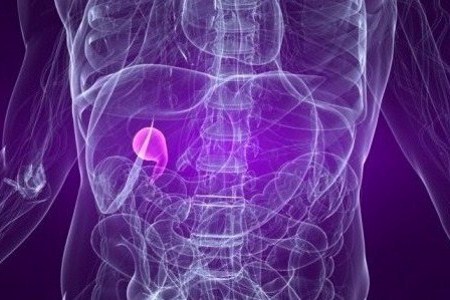
Acute Cholecystitis
Pain that occurs within minutes of eating a meal and is felt in the upper right side or upper middle of the abdomen is the main symptom of acute cholecystitis. Acute cholecystitis is a sudden inflammation of the gallbladder most often caused by gallstones.The associated pain can be sharp, cramping or dull, is intermittent and radiates to the back or below the right shoulder blade. Emergency treatment includes intravenous hydration, administration of antibiotics and surgery, if necessary. Photo: Getty Images

Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are small, hard deposits composed of mineral and acid salts that form inside the kidneys. The stones travel down the ureters, which are the tubes through which urine empties into the bladder. Kidney stones can block the flow of urine out of the kidneys. This leads to swelling of the kidney and pain. Typically, the pain is severe and starts on the side or back just below the ribs, and radiates to the lower abdomen and groin. The pain can change as the kidney stone passes through the urinary tract. Photo: Getty Images
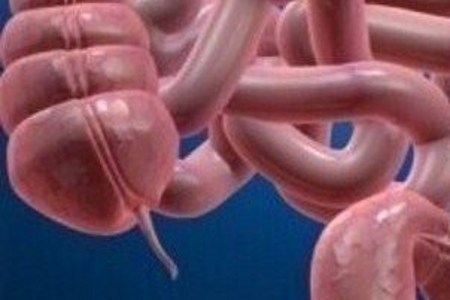
Appendicitis
Pain that begins around the navel and shift to the lower right abdomen is a warning sign of appendicitis. The pain increases in intensity over a 12 to18 hour period, becomes severe and is associated abdominal tenderness to the touch, low-grade fever, nausea and vomiting. Appendicitis is the inflammation of the appendix, a small pouch located in the lower right side of the abdomen. The inflamed appendix fills with pus. Untreated, appendicitis can lead to a ruptured appendix and an appendiceal abscess, both of which pose the serious complication of infection. Photo: Getty Images
Add a CommentComments
There are no comments yet. Be the first one and get the conversation started!